New Order Found Please Review the order ASAP for the client to
proceed

Unread Message Found Please check the message ASAP and reply to client


I. Introduction
A. Definition of Political Science Report Writing

Political Science Report Writing involves the systematic creation of documents that analyze, interpret, and present findings related to political phenomena. It is a specialized form of academic and professional writing within the field of political science, designed to communicate research outcomes and insights.
The primary purpose of these reports is to contribute to the understanding of political issues, policies, and events. A well-crafted political science report is characterized by a clear structure, evidence-based arguments, and an unbiased presentation of data. It serves as a crucial tool for scholars, policymakers, and researchers to disseminate knowledge, inform decision-making, and contribute to the ongoing discourse within the realm of political science.
B. Importance in Academic and Professional Settings
Political Science Report Writing holds paramount importance in both academic and professional settings. In academia, these reports serve as a fundamental means for students and researchers to showcase their understanding of political theories, methodologies, and empirical findings. They contribute to the scholarly dialogue by presenting original research, critical analyses, and thought-provoking insights.
Moreover, in professional contexts, political science reports play a pivotal role in informing decision-makers, policymakers, and governmental bodies about relevant issues, potential solutions, and the implications of political actions. The ability to articulate well-researched ideas in a comprehensive report format is a key skill for those engaged in political science-related professions, ensuring effective communication and influencing informed decision-making within the dynamic landscape of politics and governance.
C. Overview of Key Components
Political Science Report Writing comprises several key components essential for conveying comprehensive research and analysis. The introductory section serves to establish the report's context, presenting a clear problem statement and engaging the reader. A thorough literature review follows, offering insights into existing scholarship and framing the research within a broader academic conversation.
The methodology section outlines the research design, data collection, and analysis approaches employed in the study. The core of the report lies in the presentation and interpretation of findings, supported by statistical or qualitative evidence. A well-structured conclusion summarizes key points, highlights the report's significance, and suggests avenues for future research. Throughout, proper citation, adherence to a specific style guide, and attention to language clarity are paramount. Each component plays a vital role in creating a cohesive and impactful political science report.
II. Understanding the Basics
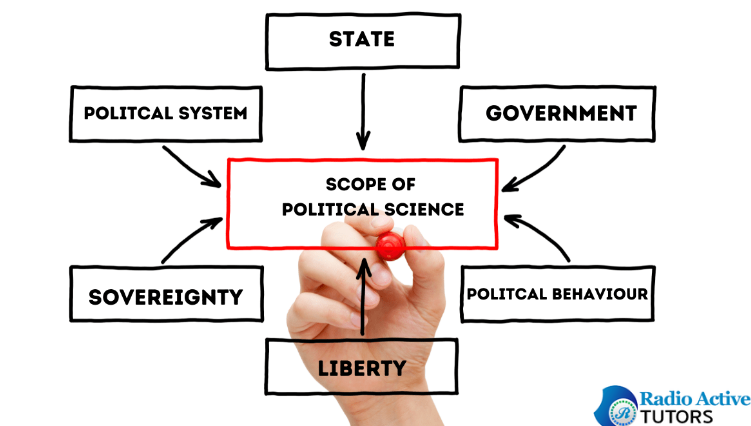
A. Purpose and Scope of Political Science Reports
Political Science Reports serve a dual purpose: to systematically investigate political phenomena and to communicate findings effectively. The primary objective is to contribute new knowledge or insights to the field of political science, whether by analyzing existing theories, exploring empirical data, or proposing novel frameworks. These reports often aim to answer specific research questions, address gaps in existing literature, or offer solutions to practical political challenges.
The scope of political science reports is broad, encompassing various subjects such as government structures, policy analyses, international relations, and political behavior. By delving into the complexities of political issues, these reports not only advance academic understanding but also provide valuable information for policymakers, stakeholders, and the wider public, influencing informed decision-making in the political arena.
1. Analytical Reports
Analytical reports represent a significant category within the realm of political science writing, characterized by their in-depth examination and interpretation of complex political issues. These reports go beyond mere description, aiming to critically analyze and evaluate the subject matter. Typically, analytical reports involve a thorough investigation of data, theories, and existing literature to offer insightful perspectives and conclusions. They often explore cause-and-effect relationships, identify patterns, and assess the implications of political phenomena.
Analytical reports are valuable tools for researchers and policymakers alike, providing a nuanced understanding of political dynamics and offering evidence-based recommendations for addressing contemporary challenges. Whether focused on policy analysis, political trends, or the consequences of specific actions, analytical reports play a crucial role in advancing knowledge and informing decision-makers in the dynamic field of political science.
2. Descriptive Reports
Descriptive reports form a vital category in political science writing, primarily concerned with providing a detailed and objective account of specific political phenomena. Unlike analytical reports that delve into the reasons and consequences of political events, descriptive reports focus on presenting an accurate portrayal of the subject matter. This involves a thorough documentation of facts, characteristics, and contextual details related to political issues, policies, or events.
Descriptive reports often serve as foundational documents, offering a comprehensive understanding of a particular situation without necessarily offering evaluative judgments. Researchers utilize descriptive reports to present a baseline of information, laying the groundwork for further analysis or comparison. Policymakers may find these reports valuable for gaining insights into the current state of affairs, enabling informed decision-making based on a solid foundation of factual data within the dynamic landscape of politics.
3. Comparative Reports
Comparative reports constitute a significant genre in political science writing, aiming to systematically assess and contrast political systems, policies, or phenomena across different contexts. These reports involve a meticulous examination of similarities and differences between two or more entities, providing valuable insights into the variations and commonalities within political structures or practices. Comparative reports often employ a structured framework for analysis, allowing researchers to draw meaningful conclusions about the factors influencing political outcomes.
Whether exploring the effectiveness of policies in different countries, comparing electoral systems, or examining governance models, these reports contribute to a deeper understanding of political dynamics on a global scale. By shedding light on the nuances of political variations, comparative reports offer valuable perspectives for policymakers, researchers, and practitioners seeking to navigate the complexities of political science.
III. Essential Elements of a Political Science Report

A. Title and Abstract
In the realm of political science report writing, the title and abstract play pivotal roles in capturing the reader's attention and providing a succinct overview of the research. The title serves as the first impression, aiming to be both informative and engaging, conveying the essence of the study. It should be carefully crafted to reflect the main focus and significance of the research. The abstract, on the other hand, serves as a concise summary of the entire report.
It encapsulates the research question, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. A well-structured abstract not only entices readers but also serves as a valuable tool for quick decision-making, helping individuals determine the report's relevance to their interests. Both the title and abstract act as crucial entry points, inviting the audience to delve into the depth and intricacies of the political science report.
B. Introduction
The introduction is a cornerstone in political science report writing, serving as the gateway to the entire document. Its primary purpose is to set the stage for the reader by providing essential context, stating the research problem, and outlining the objectives of the study. To capture the reader's interest, the introduction often begins with a compelling hook or a relevant anecdote that relates to the political issue under investigation.
It then progresses to define the scope of the report, establishing the boundaries within which the research unfolds. The introduction also articulates the significance of the research, explaining why the chosen topic is relevant and what gaps in existing knowledge it seeks to address. A well-crafted introduction not only informs the reader but also entices them to delve deeper into the subsequent sections, creating a solid foundation for understanding the political landscape explored in the report.
C. Literature Review
The literature review is a critical component within a political science report, serving as the intellectual backbone that contextualizes and informs the research. It involves a comprehensive examination of existing scholarly works, theories, and research findings related to the chosen topic. This section aims to identify key themes, debates, and gaps in the literature, providing a foundation for the current study.
By synthesizing and critiquing relevant sources, the literature review establishes the intellectual lineage of the research, demonstrating how the current investigation fits into the broader academic conversation. It not only showcases the researcher's familiarity with existing scholarship but also informs the reader about the theoretical frameworks guiding the study. A well-executed literature review is not merely a summary but a critical analysis that shapes the research questions, refines the methodology, and contributes to the overall intellectual coherence of the political science report.
IV. Crafting a Solid Methodology

A. Research Design
The research design is a pivotal aspect of crafting a robust methodology for political science reports, providing the blueprint for how the study will be conducted. In this section, researchers outline the overall strategy and structure of their investigation, addressing fundamental questions about the approach to data collection and analysis. Political science reports may adopt either a qualitative or quantitative research design, or a combination of both, depending on the nature of the research questions.
The section delves into the rationale behind the chosen design, explaining how it aligns with the objectives of the study and provides insights into the political phenomena under scrutiny. Details about sampling techniques, data collection instruments, and the overall framework for analysis are crucial components within the research design, ensuring transparency and reproducibility. A well-crafted research design enhances the credibility of the political science report, enabling readers to understand and evaluate the methodological rigor applied to generate meaningful insights.
1. Qualitative vs. Quantitative Approaches
When crafting the research design for political science reports, researchers must make critical decisions regarding the methodology employed, often choosing between qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative research focuses on exploring in-depth insights, employing methods such as interviews, case studies, and content analysis to uncover nuanced aspects of political phenomena.
On the other hand, quantitative research relies on statistical methods, utilizing surveys, experiments, and numerical data to establish patterns and relationships. The choice between these approaches hinges on the research questions at hand, with qualitative methods providing rich context and understanding, and quantitative methods offering statistical rigor and generalizability. A judicious combination of both approaches, known as mixed methods, is also common, allowing researchers to harness the strengths of each methodology. Ultimately, the chosen research design shapes the nature and depth of insights in political science reports, influencing the overall quality and applicability of the research findings.
2. Sampling Techniques
In the realm of political science reports, the choice of sampling techniques is a pivotal aspect of research design. Sampling involves selecting a subset of individuals or cases from a larger population for study, aiming to draw valid and representative conclusions. Probability sampling methods, such as simple random sampling and stratified sampling, ensure that each element in the population has an equal chance of being included, enhancing the generalizability of findings.
Non-probability sampling methods, including convenience sampling and purposive sampling, are often employed when practical constraints or specific research objectives dictate a targeted approach. The selection of an appropriate sampling technique is integral to the validity and reliability of the study's results, ensuring that the sample accurately reflects the characteristics of the broader population under investigation in political science research.
B. Data Collection
Within the methodology of political science reports, the process of data collection is a crucial phase that determines the quality and reliability of the study's findings. This section outlines the systematic gathering of information to address the research questions or test hypotheses. Depending on the nature of the study, data collection methods may include surveys, interviews, content analysis, archival research, or observations.
The choice of data collection instruments is justified, detailing how these methods align with the research objectives and the selected research design. Researchers also consider ethical considerations, ensuring the protection of participants and the integrity of the study. The transparency and clarity in describing the data collection process enhance the report's credibility, allowing readers to assess the validity and generalizability of the findings. A meticulous approach to data collection is fundamental in producing insightful and robust political science reports.
V. Data Analysis and Interpretation

A. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis is a cornerstone of the data analysis and interpretation phase in political science reports, providing a systematic approach to making sense of collected data. This section employs various statistical techniques to uncover patterns, relationships, and trends within the dataset. Researchers use descriptive statistics to summarize and present key features of the data, such as means, frequencies, and distributions.
Inferential statistics are then applied to draw conclusions about the broader population based on the sample data, using methods like hypothesis testing and regression analysis. The rationale behind the chosen statistical tools is thoroughly explained, ensuring transparency in the analytical process. Visual aids, such as charts and graphs, are often employed to enhance the presentation of statistical findings. A meticulous and well-justified statistical analysis strengthens the validity of the study's conclusions, contributing to the overall rigor and credibility of the political science report.
In the realm of political science reports, qualitative analysis stands as a powerful method for interpreting and understanding complex political phenomena. This section delves into the in-depth examination of non-numerical data, such as textual information from interviews, documents, or open-ended survey responses. Qualitative analysis involves systematic procedures like coding, categorization, and theme identification to extract meaningful insights and patterns from the data.
Researchers often employ various approaches such as content analysis, grounded theory, or narrative analysis, depending on the nature of the study. The emphasis here is on exploring the richness and nuances of political contexts, capturing the depth and complexity that quantitative methods may not fully convey. By presenting quotes, excerpts, or case studies, qualitative analysis adds a human dimension to the data, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the political issues under investigation. A well-executed qualitative analysis enhances the overall robustness of the political science report, providing a holistic perspective on the researched phenomena.
1. Coding and Theme Identification
In the realm of political science report writing, developing a coherent structure is paramount, and a key aspect of this structure is the effective presentation of arguments. Each section should unfold logically, with a clear introduction that sets the stage for the reader. Subsequent segments must present arguments in a systematic manner, ensuring a seamless flow from one idea to the next.
Headings and subheadings play a vital role in guiding the reader through the narrative, helping to organize and delineate various aspects of the presented arguments. By maintaining a logical progression, political science writers can ensure that their arguments are not only persuasive but also accessible, contributing to a well-structured and impactful report.
2. Drawing Conclusions
In the process of developing a coherent structure for a political science report, drawing conclusions emerges as a crucial component. The conclusion serves as the culmination of the presented arguments, providing a synthesis of key findings and insights. This section should not merely recapitulate information but rather offer a nuanced interpretation of the research outcomes.
It is an opportunity for political science writers to underscore the significance of their work, elucidate implications, and suggest potential avenues for future exploration. By ensuring a thoughtful and cohesive conclusion, writers can leave a lasting impact, leaving readers with a clear understanding of the study's contributions to the broader field of political science.
VI. The Art of Effective Writing

A. Developing a Coherent Structure
Creating a coherent structure is an essential aspect of mastering the art of effective writing in political science reports. This section focuses on organizing the report in a logical and reader-friendly manner to enhance comprehension and engagement. The structure typically includes an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction serves to capture the reader's attention, articulate the research problem, and outline the objectives. The body comprises clear and well-organized sections, each dedicated to a specific aspect of the research.
This includes presenting arguments, supporting them with evidence, and maintaining a logical flow between paragraphs and sections. Headings and subheadings play a crucial role in guiding the reader through the content. The conclusion succinctly summarizes key findings, reiterates the report's significance, and often suggests avenues for future research. A coherent structure not only facilitates understanding but also reflects the researcher's mastery in presenting complex political science insights in a clear and accessible manner.
B. Citation Styles in Political Science
Accurate and consistent citation is a fundamental aspect of effective writing in political science reports. This section navigates the nuances of citation styles, with a focus on the commonly used formats such as APA (American Psychological Association) and MLA (Modern Language Association). Researchers must adhere to specific citation guidelines to give credit to the original sources of information and ideas, ensuring academic integrity and avoiding plagiarism.
The section elucidates the intricacies of citing various sources, including books, articles, government documents, and online resources, each with its own set of rules. Understanding the importance of citation styles not only reflects the writer's commitment to scholarly conventions but also facilitates the replication of the study and fosters a seamless scholarly conversation within the field of political science. A mastery of citation styles is integral to the art of effective writing, demonstrating the writer's attention to detail and commitment to maintaining the highest standards of academic rigor.
VII. Engaging the Reader

A. Creating Compelling Headings and Subheadings
Capturing and maintaining the reader's interest is a key aspect of effective political science report writing, and the strategic use of compelling headings and subheadings plays a vital role in this endeavor. This section focuses on the art of crafting headings that are not only informative but also intriguing. Headings should provide a snapshot of the content, guiding the reader through the narrative and signaling the key points of each section.
Subheadings further break down complex information, enhancing readability and facilitating comprehension. A judicious combination of clarity and creativity in crafting headings can transform the reading experience, making the report more accessible and engaging. By strategically organizing information into well-designed headings and subheadings, writers can effectively communicate the report's structure, guide the reader's attention, and ultimately enhance the overall impact and accessibility of the political science document.
B. Using Visuals for Impact
The integration of visuals is a powerful strategy for enhancing reader engagement in political science reports. This section explores the diverse ways in which visuals such as charts, graphs, and infographics can be employed to convey complex information effectively. Visuals not only break up the monotony of text but also offer a dynamic means of presenting data, making it more accessible and comprehensible for a broader audience.
The strategic use of visuals can elucidate trends, highlight key findings, and provide a visual narrative that complements the written content. Researchers must choose visuals that align with the report's objectives, ensuring they enhance rather than distract from the message. This section also delves into considerations for designing visually impactful elements, such as choosing appropriate formats, labeling, and ensuring accessibility. By incorporating visuals thoughtfully, political science reports can significantly elevate their impact, making the content more engaging, memorable, and conducive to effective communication.
VIII. Addressing Common Challenges

A. Writer's Block
Writer's block can be a formidable obstacle in the process of crafting political science reports. This section explores effective strategies for overcoming this common challenge and maintaining a productive writing flow. Acknowledging that writer's block often stems from factors like anxiety, perfectionism, or lack of clarity, the section offers practical solutions. Techniques such as freewriting, breaking down the writing process into smaller tasks, and setting realistic goals can help writers overcome mental barriers and initiate the writing process.
Emphasizing the importance of embracing imperfection in initial drafts, the section encourages writers to focus on generating ideas and content, with refinement to come in subsequent revisions. Additionally, incorporating regular breaks, changing the writing environment, and seeking feedback from peers or mentors can contribute to breaking through writer's block and fostering a more conducive writing experience in the realm of political science reports.
B. Handling Extensive Research
Navigating the complexities of extensive research poses a common challenge in political science report writing. This section explores effective strategies for managing large volumes of information, ensuring that the research process remains organized and the final report is coherent. It begins by emphasizing the importance of systematic organization, recommending tools like reference management software to efficiently catalog and retrieve sources.
Breaking down the research into manageable segments, setting realistic milestones, and creating a structured outline can help writers maintain focus and clarity. The section also advocates for strategic note-taking, emphasizing the extraction of key information and ideas during the research phase. Collaboration with peers, advisors, or research teams can provide valuable perspectives and support in handling extensive research. By implementing these strategies, writers can navigate the challenges of extensive research, resulting in a well-organized and comprehensive political science report.
C. Ensuring Objectivity in Reporting
Maintaining objectivity is a paramount challenge in political science reports, as researchers strive to present information free from personal bias or undue influence. This section explores strategies to uphold objectivity throughout the research and writing process. It emphasizes the importance of clearly defining research questions and hypotheses at the outset, ensuring that the study remains focused and unbiased.
Researchers are encouraged to critically evaluate sources, considering diverse perspectives and minimizing potential biases in the selection of data. Transparent reporting of methodologies, including any limitations or potential sources of bias, is crucial for establishing credibility and demonstrating a commitment to objectivity. Peer review and collaboration with colleagues can also serve as checks against subjective interpretations. By adopting these strategies, writers can navigate the challenge of ensuring objectivity in political science reports, contributing to the production of rigorous and impartial analyses within the field.
IX. Fine-Tuning Your Language

A. Writing Clearly and Concisely
Clarity and conciseness are indispensable elements in effective political science report writing. This section delves into the art of crafting clear and concise prose to enhance the communication of complex political concepts. It emphasizes the importance of avoiding unnecessary jargon and convoluted sentences, opting instead for straightforward language that ensures the reader can readily grasp the intended meaning.
The section explores techniques such as active voice, precise terminology, and well-structured sentences to enhance clarity. Additionally, it encourages writers to consider their audience, balancing the need for accuracy with the necessity of making the content accessible to a broader readership. Through meticulous language choices, political science reports can convey information with precision and impact, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter among diverse audiences.
B. Avoiding Jargon and Ambiguity
Effectively communicating complex political ideas necessitates a conscious effort to avoid jargon and ambiguity in political science reports. This section explores the significance of using clear and accessible language to ensure that the report's content is comprehensible to a diverse audience. It encourages writers to steer clear of discipline-specific terminology that may hinder understanding, opting instead for plain language without sacrificing precision.
By providing clear definitions or explanations for specialized terms, writers can strike a balance between accuracy and accessibility. Ambiguity, often stemming from vague language or imprecise expressions, can be mitigated by choosing words with clear meanings and by carefully articulating concepts. The section underscores the importance of clarity in language as an essential tool for engaging readers, promoting understanding, and enhancing the overall impact of political science reports.
C. Proofreading and Editing Tips
Proofreading and editing are indispensable stages in the refinement of political science reports, ensuring clarity, coherence, and professional presentation. This section explores effective strategies for meticulously reviewing and enhancing written content. It advocates for a structured approach, advising writers to begin with a comprehensive review of overall structure, coherence, and flow. Attention to grammar, punctuation, and spelling is essential to maintain linguistic precision.
The use of professional proofreading tools or seeking feedback from peers can provide an additional layer of scrutiny. Addressing issues of clarity and eliminating redundancies enhances the overall readability of the report. Additionally, taking breaks between writing and proofreading sessions can provide a fresh perspective, aiding in the identification of errors or areas for improvement. By incorporating these proofreading and editing tips, political science reports can achieve a polished and refined quality, elevating the overall impact of the written work.
X. Political Science Reports in the Digital Age

A. Leveraging Technology for Research
The advent of the digital age has revolutionized the landscape of political science research, offering innovative tools and methodologies that significantly enhance the research process. This section explores how researchers can effectively leverage technology to advance their studies within the realm of political science reports. It delves into the use of online databases, academic search engines, and digital archives, emphasizing the accessibility and efficiency these resources provide in gathering relevant literature and data.
The section also discusses the integration of data analysis software and statistical tools, facilitating robust quantitative research. Moreover, it explores the advantages of utilizing digital platforms for surveys, interviews, or collaborative research projects, transcending geographical boundaries and fostering international collaborations. As technology continues to evolve, political science reports can benefit from embracing these advancements, fostering a more streamlined, interconnected, and dynamic approach to research in the digital age.
B. Online Resources for Political Science Writers
In the digital age, political science writers benefit from a plethora of online resources that significantly augment their research capabilities. Academic databases such as JSTOR and Google Scholar serve as virtual treasure troves, offering a vast array of scholarly articles and research papers. Tools like Zotero and EndNote streamline the citation process, ensuring efficient organization of sources.
Online writing communities and social media platforms like Twitter and LinkedIn provide spaces for networking, collaboration, and staying abreast of the latest developments in the field. Additionally, platforms like Coursera and edX offer online courses, enabling writers to continually enhance their skills. Embracing these online resources empowers political science writers to navigate the digital landscape effectively, fostering collaboration, staying informed, and honing their craft in the dynamic realm of political science research and reporting.
XI. Conclusion
A. Recap of Key Takeaways
In conclusion, this comprehensive guide has navigated the intricate landscape of political science report writing in the digital age. Throughout, we've explored fundamental elements, from crafting compelling introductions to leveraging technology for research. As we wrap up, it's crucial to recap key takeaways. Emphasizing the significance of clarity, writers are encouraged to communicate complex ideas with simplicity, avoiding jargon and ambiguity. Leveraging online resources and technological tools enhances efficiency and connectivity in the research process.
The importance of objectivity, proofreading, and fine-tuning language has been underscored, ensuring the production of credible and polished reports. Whether addressing challenges like writer's block or handling extensive research, the guide has provided strategies for overcoming obstacles. As political science writers embark on their journey, these key takeaways serve as valuable guideposts, fostering a nuanced, impactful, and technologically savvy approach to political science report writing.

Hard Binding Dissertation ( 4 Key Features)
5 month(s) ago
Psychology dissertation topics (5 Major Areas)
5 month(s) ago
Dissertation editor (5 Key Services)
5 month(s) ago
Dissertation Coaching (7 Main Benefits)
5 month(s) ago
Dissertation Acknowledgement Format ( 6 Key Tips)
5 month(s) ago
Psychology Dissertation Topics ( 7 Main Ideas)
5 month(s) ago
Dissertation Binding ( Key Tips)
5 month(s) ago
Dissertation editing services (8 Key Areas)
5 month(s) ago
Dissertation template (Student's Guide)
5 month(s) ago
How to come up with a dissertation topic (9 Key Steps)
5 month(s) ago
Radio Active Tutors is a freelance academic writing assistance company. We provide our assistance to the numerous clients looking for a professional writing service.
Need academic writing assistance ?
Order Now
