Market analysis is a foundational process in business strategy, providing invaluable insights into the dynamics of a specific industry, target audience, and competitive landscape. This comprehensive examination of the market ecosystem empowers businesses to make informed decisions, tailor their offerings, and seize opportunities effectively. By delving into the core components of market analysis, including its purpose, key elements, methods, and benefits, we can uncover the significance of this process in shaping successful business endeavors.

Purpose of Market Analysis:
At its core, market analysis aims to provide businesses with a deep understanding of the external factors that influence their operations. This understanding is instrumental in shaping strategies, making informed decisions, and identifying potential pitfalls. Whether a business is launching a new product, expanding into new markets, or seeking to refine its current offerings, market analysis helps mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
Key Elements of Market Analysis:
- Market Size and Growth: Understanding the overall size of the market and its potential for growth is essential. This involves assessing historical data, current trends, and future projections to gauge the market's trajectory.
- Target Audience: Identifying the specific demographics, preferences, needs, and behaviors of the target audience is crucial. A thorough understanding of the audience ensures that marketing efforts and product development align with their expectations.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyzing competitors provides insights into their strengths, weaknesses, strategies, and market positioning. This knowledge allows businesses to differentiate themselves effectively and identify gaps in the market.
- Market Trends: Staying attuned to market trends, including technological advancements, cultural shifts, and consumer preferences, helps businesses anticipate changes and adapt proactively.
- Regulatory and Legal Factors: Understanding the regulatory environment is vital for compliance and risk management. Regulations can impact product development, distribution, and marketing strategies.
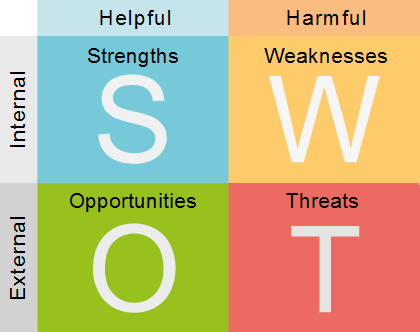
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) helps identify internal strengths and weaknesses as well as external opportunities and threats, providing a holistic view of the business's position in the market.
- Market Segmentation: Dividing the market into segments based on factors like demographics, psychographics, and behaviors allows for tailored marketing strategies that resonate with specific groups.
- Entry Barriers: Identifying potential barriers to entry, such as high startup costs, regulatory hurdles, or established competitors, helps businesses assess the feasibility of entering a new market.
Methods of Market Analysis:
Market analysis involves a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods to gather and interpret relevant data. Some common methods include:
1. Primary Research:
Primary research involves collecting firsthand data directly from the target audience or relevant stakeholders. This method provides valuable insights into consumer behavior, preferences, opinions, and needs. There are several techniques within primary research:
- Surveys: Surveys involve creating structured questionnaires that respondents fill out. Surveys can be conducted online, in-person, or over the phone. They are effective for gathering quantitative data and measuring customer opinions on various topics.
- Interviews: Interviews involve engaging participants in one-on-one discussions to gather qualitative insights. Interviews allow for in-depth exploration of ideas, opinions, and experiences. They are especially useful for understanding complex decision-making processes.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups involve a small group of participants discussing specific topics facilitated by a moderator. These discussions offer qualitative insights and reveal group dynamics and shared perceptions.
- Observations: Observations involve directly watching and recording consumer behavior without direct interaction. This method is particularly useful for understanding real-time behaviors in physical spaces, such as retail environments.
2. Secondary Research:
Secondary research involves gathering information from existing sources such as published reports, industry studies, academic papers, and data from governmental and non-governmental organizations. Secondary research is cost-effective and provides a broader context for market analysis. Some sources of secondary data include:
- Industry Reports: Reports published by market research firms provide comprehensive insights into industry trends, market size, growth projections, and competitive analysis.
- Market Studies: Academic research studies and reports from industry associations can offer valuable data on consumer behavior, market dynamics, and emerging trends.
- Government Data: Government agencies often provide data on economic indicators, demographics, and market trends. These sources are reliable and authoritative.
- News and Media: News articles, press releases, and industry blogs can provide current insights into market developments, consumer sentiment, and emerging technologies.
3. Competitor Analysis:
Analyzing competitors is a crucial aspect of market analysis. This method involves studying the strategies, products, pricing, and market positioning of existing and potential competitors. Some techniques for competitor analysis include:
- SWOT Analysis: Conducting a comprehensive SWOT analysis helps identify competitors' strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This analysis offers insights into their strategic position and potential vulnerabilities.
- Benchmarking: Benchmarking involves comparing your business's performance against key performance indicators (KPIs) of competitors. This helps identify gaps and areas for improvement.
- Mystery Shopping: Mystery shopping entails posing as a customer to experience competitors' products or services firsthand. This provides insights into their customer experience, pricing strategies, and service quality.
- Online Research: Studying competitors' websites, social media profiles, customer reviews, and marketing campaigns can reveal valuable information about their strategies and customer engagement.
4. Data Analysis:
Data analysis involves processing and interpreting quantitative data to uncover patterns, trends, and insights. This method relies on data collected from various sources, such as sales data, customer behavior data, and online analytics. Common data analysis techniques include:
- Statistical Analysis: Using statistical methods to analyze numerical data, such as calculating averages, percentages, correlations, and regression analyses.
- Data Visualization: Creating graphs, charts, and dashboards to visually represent data trends and patterns. Visualization makes complex data more understandable and actionable.
- Segmentation Analysis: Dividing data into segments based on variables such as demographics or behaviors to uncover specific insights about different customer groups.
- Predictive Analysis: Using historical data to make predictions about future trends, customer behavior, and market dynamics.
Incorporating a mix of these methods allows businesses to gain a well-rounded and comprehensive understanding of the market. Each method offers unique insights into consumer behavior, industry trends, competition, and opportunities, ultimately guiding businesses towards effective strategies and decisions.
Benefits of Market Analysis:

Informed Decision-Making: Market analysis provides a factual basis for decisions, reducing guesswork and increasing the likelihood of success.
Risk Mitigation: By identifying potential challenges and threats, businesses can proactively develop strategies to mitigate risks.
Resource Allocation: Market analysis guides efficient resource allocation by pinpointing areas with the highest potential for returns.
Customer-Centric Approach: Understanding customer needs and preferences enables businesses to tailor their products and services, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Competitive Advantage: Identifying gaps in the market and differentiating from competitors can lead to a unique selling proposition.
Innovation: Insights from market analysis can inspire innovation by highlighting unmet needs or emerging trends.
Expansion Opportunities: When considering new markets, market analysis ensures a comprehensive understanding of the local dynamics and consumer behavior.
Conclusion:
Market analysis is not just a preliminary step but an ongoing process that informs every stage of a business's lifecycle. In an ever-evolving business landscape, understanding market dynamics is essential for survival and growth. By examining the market's size, growth potential, target audience, competition, and trends, businesses can craft strategies that resonate with their customers and leverage opportunities effectively. Market analysis is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to navigate complexity, make informed decisions, and thrive in competitive environments.
