Introduction
Mind maps are powerful tools that can significantly enhance a student's ability to understand, organize, and retain information. They provide a visual representation of complex concepts, making it easier to grasp the relationships between different ideas. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits of mind mapping for students, the key elements of a successful mind map, and step-by-step instructions on how to create effective mind maps for various educational purposes.
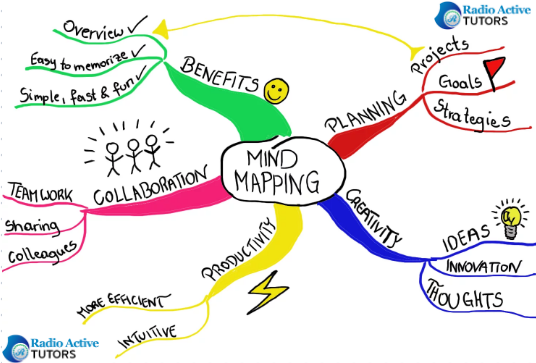
I. Understanding the Benefits of Mind Mapping for Students
Improved Learning and Retention
Mind maps help students’ process information more effectively by engaging both the left and right hemispheres of the brain. The combination of words and images creates a more memorable and holistic learning experience.
Enhanced Organization
Mind maps allow students to structure and categorize their thoughts, making it easier to identify key concepts and their interconnections.
Creative Thinking
Mind mapping encourages creative thinking and problem-solving. Students can make connections between ideas that might not be obvious in traditional note-taking methods.
Effective Revision
When preparing for exams, students can use mind maps to review and consolidate their knowledge, helping them recall information more easily.
Improved Communication
Mind maps can serve as an effective communication tool, allowing students to present their ideas in a clear and visually appealing way.
II. Key Elements of a Successful Mind Map

Central Idea or Topic
Every mind map begins with a central idea or topic placed at the center of the page. This idea is the focal point of the map and should be concise and clear.
Branches
Branches radiate from the central idea and represent the main categories or themes related to the topic. These branches act as the primary organizational structure of the mind map.
Sub-branches
Sub-branches extend from the main branches and further categorize and detail the information. These sub-branches can continue to branch out as needed to create a hierarchy of information.
Keywords and Images
Each branch and sub-branch should include keywords and, if possible, relevant images or symbols. Keywords serve as a shorthand for concepts, making the mind map more concise and visual.
Color and Formatting
Color can be used to differentiate between branches, sub-branches, and keywords. Using a consistent and visually appealing color scheme can help students remember and understand the information better.
Use of Lines and Arrows
Lines and arrows connect different elements in the mind map, indicating relationships, dependencies, or sequences. They can be used to show cause-and-effect, chronology, or other connections between ideas.
White Space
Adequate white space ensures that the mind map is not overcrowded and overwhelming. It helps maintain clarity and makes it easier to navigate the map.
III. Step-by-Step Guide to Creating Mind Maps for Students

Now that we have discussed the benefits and key elements of a successful mind map, let's dive into the step-by-step process of creating mind maps for students.
- Select a Topic or Subject
Choose the topic or subject you want to create a mind map for. This could be a specific lesson, a textbook chapter, a research project, or any other area of study. Make sure the topic is well-defined and manageable.
- Gather Your Materials
To create a mind map, you will need some materials:
Paper or a blank document on your computer.
Writing and drawing tools such as colored pens, pencils, or digital drawing software.
- Start with the Central Idea
Write the central idea or topic at the center of the page. It should be a concise and clear statement that represents the main focus of your mind map.
- Identify Main Branches
Think about the main categories or themes related to your topic. These will become the main branches of your mind map. Draw lines radiating outward from the central idea and label them with the main branches.
- Add Sub-branches
For each main branch, consider the subtopics or details that belong to that category. Create sub-branches that extend from the main branches and label them accordingly. These sub-branches can continue to branch out as needed to represent more specific information.
- Use Keywords and Images
In each branch and sub-branch, include keywords that summarize the concepts or information. If appropriate, add images or symbols that visually represent the ideas. This combination of words and images enhances memory and understanding.
- Use Color and Formatting
Assign a color to each main branch and its corresponding sub-branches. Be consistent with your color scheme to maintain clarity. Use bold and clear formatting to make your mind map visually appealing.
- Connect Ideas with Lines and Arrows
Use lines and arrows to connect different elements of your mind map. These connections can represent relationships, sequences, or dependencies between ideas. Be sure to label the lines or arrows to clarify their purpose.
- Create White Space
Ensure that your mind map is not overcrowded. Leave ample white space around your branches and sub-branches to maintain a clear and organized structure.
- Review and Refine
After creating the initial draft of your mind map, review it for clarity and accuracy. Make any necessary refinements, such as adjusting the layout, adding or removing elements, or reorganizing branches for better flow.
- Use Digital Mind Mapping Tools
While creating hand-drawn mind maps is effective, digital mind mapping tools offer additional benefits, such as the ability to easily rearrange and expand branches. Popular digital mind mapping software includes MindMeister, XMind, and Coggle.
IV. Applying Mind Maps in Various Educational Scenarios

Mind maps can be applied to a wide range of academic scenarios to aid students in learning, understanding, and retaining information. Here are some common educational contexts where mind maps are beneficial:
Note-Taking
Students can use mind maps as an alternative to traditional linear note-taking methods. When attending lectures or reading textbooks, they can create mind maps to capture and visualize key points, concepts, and relationships between ideas.
Study and Revision
Mind maps are excellent tools for reviewing and revising subjects before exams. By creating mind maps that condense and simplify complex topics, students can better absorb and recall information.
Research and Project Planning
Mind maps are invaluable for organizing research materials, brainstorming ideas, and planning projects. They help students structure their thoughts, identify research gaps, and ensure that their work follows a logical sequence.
Problem Solving
Mind maps promote creative thinking and problem-solving. Students can use them to break down complex problems into manageable components, identify potential solutions, and explore connections between different approaches.
Group Work and Collaboration
Mind maps facilitate collaboration in group projects. They allow team members to visualize the project's structure, allocate tasks, and ensure that everyone understands their role within the larger context.
Presentation and Communication
Students can use mind maps to prepare and deliver presentations. Mind maps serve as visual aids that make it easier for the audience to grasp complex information.
V. Tips for Creating Effective Mind Maps
Creating a mind map is an art, and there are several tips and techniques that can help students maximize the effectiveness of their mind maps:
Keep It Simple
Avoid overcomplicating your mind map. Use concise keywords and simple, clear lines. The goal is to enhance understanding, not confuse the reader.
Prioritize Information
Highlight the most important or relevant information by placing it at the center or on top of the mind map. This helps draw the reader's attention to key concepts.
Use Visual Elements
Incorporate images, icons, and symbols that are relevant to the topic. Visual elements can make your mind map more engaging and memorable.
Experiment with Layouts
While the traditional radial layout is common, feel free to experiment with different layouts like hierarchical, tree-like structures, or even circular mind maps. Choose the layout that best suits the content and your personal preferences.
Use Consistent Formatting
Stick to a consistent color scheme, font, and formatting style to make your mind map look polished and organized.
Engage Multiple Senses
When creating a mind map, engage multiple senses. Draw, write, and use colors. The tactile experience can enhance memory retention.
Review and Refine
Periodically revisit your mind map to ensure that it accurately represents your understanding of the topic. Update it as you gain more knowledge and insights.
Customize for Learning Style
Adapt your mind map to your personal learning style. Some students may prefer a more linear and structured mind map, while others may benefit from a more creative and visual approach.
Practice Regularly
Like any skill, creating effective mind maps improves with practice. Make it a regular part of your study routine to hone your mind mapping skills.
Seek Inspiration
Explore existing mind maps and templates to get inspiration for your own creations. There are numerous resources and examples available online.
VIII. Conclusion
Mind maps are versatile and powerful tools that can greatly benefit students in various academic contexts. By providing a visual representation of information and encouraging creative thinking, mind maps enhance learning, organization, and retention. Following the key elements of a successful mind map and using the step-by-step guide outlined in this comprehensive guide, students can create effective mind maps to support their academic endeavors. With practice and adaptation to their individual learning styles, students can unlock the full potential of mind mapping for their education.
